More people are turning to cannabis than ever before because of its many healthful effects. At the same time, an ever-growing number of people are cultivating various strains of marijuana to help consumers take full advantage of this long-used herb. Understanding all the components of cannabis and how they work is the key to maximizing their benefits.
At Kind Seed Co, we offer a vast selection of cannabis seeds to local growers in Oklahoma and throughout the rest of the country. Each strain in our inventory offers its own unique range of aromas, flavors, and effects. These come from the complex and diverse compounds found in each strain.
Marijuana contains hundreds of components. You are probably familiar with THC and CBD, the two primary cannabinoids, but they are only the tip of the iceberg. More than 100 others have been discovered over the years as well. These include CBN, CBG, THCV, and CBDA to name a few.
Cannabis is also loaded with other compounds, over 200 of which are terpenes. These are the ones we are going to focus on right now. They provide certain beneficial effects on their own, but when combined with THC and CBD, they all work together to ramp up weed’s power and create an entirely different level of positive influences.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are an elite class of compounds found in cannabis as well as all other plants. Technically, they are classified as hydrocarbons, meaning they are compounds that consist of hydrogen and carbon. That said, each terpene has a unique chemical composition and an exclusive scent, flavor, and assortment of benefits.
On a basic level, terpenes are a plant’s essential oils. You have experienced them all your life whether you realize it or not. When you bite into a luscious, juicy orange or a ripe, velvety banana, you are smelling and tasting the terpenes. If you pass by a rose garden and the bold, beautiful aroma invades your senses, that is the terpenes at work. When you bring in a live Christmas tree to decorate, its terpenes are what make your home smell like the holidays.
All plants contain terpenes. They are not unique to marijuana. Cannabis and other fruits, flowers, vegetables, and trees even share some of the same terpenes. Many terpenes are present in different strains of cannabis as well, but the varying types, amounts, and concentrations work in tandem with the cannabinoids in each strain to create and reinforce its benefits.
How Are Terpenes Made?
Plants make terpenes naturally as they grow. Cannabis, in particular, begins to take in moisture, heat, light, nutrients, and carbon dioxide as soon as its genetic material breaks free from the protective shell of its seed. As the plants use all those essential elements to make food, they are also using them to create THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids. Terpenes, flavonoids, and other compounds also develop along the way.
Like cannabinoids and other compounds, terpenes are present throughout the cannabis plant. They are more highly concentrated in the buds, though. When you harvest those buds, you are gathering all the compounds they hold in store, including the terpenes.
Several factors affect terpene concentration in plants. Their growing conditions are the most important aspects. Specific genetics in each cannabis strain determine the types of terpenes that will be present as well as their strength and effectiveness.
It is also fair to mention that terpenes are being created artificially these days. They are made in a lab as opposed to developing naturally within a plant. Some sources insist they are safe, but others paint a different picture. Certain synthetic cannabinoids and terpenes have been taken off the market due to their potential dangers.
Synthetic terpenes generally taste and smell stronger than their natural counterparts. Still, they are not real. You could compare synthetic and natural cannabis terpenes to the differences between eating a grape and drinking a grape soda or munching on fresh strawberries as opposed to eating strawberry-flavored candy.
Many reports show that synthetic terpenes may not be as effective as natural ones in their usefulness as well. They may provide some of the same benefits, but they do not have quite the same well-rounded profile.
Hundreds or even thousands of compounds exist together in marijuana plants, but scientists can only isolate and recreate about 40 of them. That means linalool or myrcene developed in a lab will not have the same accompanying compounds as it would coming from nature.
Hundreds or even thousands of compounds exist together in marijuana plants, but scientists can only isolate and recreate about 40 of them. That means linalool or myrcene developed in a lab will not have the same accompanying compounds as it would coming from nature.
You have probably heard of terpenes considering the amount of talk they are generating in the world of cannabis. You may have also heard the term used interchangeably with terpenoids. In reality, terpenes and terpenoids both exist, but they are two entirely separate elements.
Terpenes are cannabis compounds in their natural form. As mentioned, they are made up of hydrogen and oxygen. As long as these components remain in their natural, unaltered state, they are considered terpenes.
Terpenoids are terpenes that have been changed in some way. In most cases, the transformation from terpenes to terpenoids occurs during the extraction or drying process. Any factor that somehow alters the chemical composition of a terpene after harvesting the plants that created it causes it to become a terpenoid.
That is not to say terpenoids are bad or less desirable. They are still essentially the same types of compounds they were before being denatured by heat or other factors. They may be a bit less potent than in the beginning. Of course, since they have extra atoms and functional characteristics, some may be more beneficial and offer a broader range of effects.
What Role Do Terpenes Serve?
Terpenes serve numerous roles both before and after harvest. We have to understand that plants produce them during their growth cycles for a reason. That reason really has nothing to do with how humans can benefit from the compounds after all those ripe buds are harvested.
From the Plants’ Point of View
Some terpenes are tasked with deterring predators and diseases. Pests are drawn to certain smells and flavors. That is why they attack so many trees and garden plants.
They are not particularly fond of other aromas and tastes, which is where specific cannabis terpenes come into play. Many diseases and fungi feed off of certain botanical components, making plants vulnerable to pathogens. Terpenes help ward off those invaders and keep the plants healthy.
Other terpenes are responsible for attracting pollinators, like bees. Those terpenes have just the right scents and tastes to encourage pollinators to visit cannabis plants once they begin to mature. Then, they pick up pollen from male marijuana plants and deliver it to female flowers, so they will produce seeds to grow new plants.
Post-Harvest Terpene Functions
As we have already discussed, terpenes give each strain of marijuana its unique flavor and aroma. You have probably noticed that the better a food or beverage smells, the better it tastes. At the same time, the way it smells affects the way it tastes. Terpenes make cannabis buds smell stronger and taste better when they are present in the right concentrations.
In addition to enhancing the aroma and flavor of cannabis, terpenes offer a wide range of medicinal benefits. Some have antibacterial properties whereas others are antiviral. Many others help relieve pain and inflammation, through mechanisms that are only partially understood.
Certain terpenes alleviate anxiety and depression. Studies show some may even act as neuroprotectors to ward off Alzheimer’s and other degenerative disorders. For all the recreational marijuana users in the world, some terpenes can even enhance the high each THC-laden strain provides.
How Terpenes Work
Like cannabinoids, terpenes provide their beneficial effects by binding to or interacting with neurotransmitters and receptors throughout the brain and body. They may reduce the body’s reaction to serotonin or weaken various pain receptors. They might increase dopamine and norepinephrine production or intercept glutamate before it has a chance to transmit pain signals from the body to the brain. Each terpene acts in a different way.
Co-Existing in Harmony
On top of those benefits, terpenes work with cannabinoids and flavonoids to increase their influences. This is known as the Entourage Effect. If you remove the terpenes from cannabis buds, the CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids that are left behind will not be as effective. On the other hand, the extracted terpenes will not be as powerful on their own as they would be with their naturally accompanying cannabinoids.
What Are the Major Terpenes?
Hundreds of terpenes have been discovered in cannabis plants. Some are more prominent than others. They generally exist in higher concentrations and show up across more strains than other terpenes. We will discuss them in further detail later on, but this is a basic rundown of the major contenders.
- Myrcene
- Pinene
- Linalool
- Humulene
- Limonene
These are a few of the basic and most common terpenes, but they barely scratch the surface. Keep in mind, science has barely begun to explore the world of terpenes, and many of them have yet to be discovered and studied. Now, let us take a look at how some of these terpenes relate to different marijuana strains.
Delving into the Different Cannabis Strains
It is no secret that three basic strains of cannabis exist in nature: Sativa, Indica, and Ruderalis. Each strain has a general terpene profile though the specific composition of the different strains within those categories varies greatly. Terpenes found in each strain determine its flavor, aroma, benefits, and other aspects that impact its medicinal usefulness.
Dissecting Sativas
In terms of physical appearance, Sativas tend to be tall and lanky. They are usually lighter in color than other strains and have thinner leaves. Their buds are longer and slenderer than those of their cousins. Sativas originally hail from warmer climates like Central America and Southeast Asia. They love heat and are accustomed to long hours of strong sunlight.
Sativas are widely known for their energetic, euphoric impacts. Part of this effect comes from their typical levels of THC. Still, terpenes are largely responsible for the inclusive influence as well. Sativas often contain high concentrations of limonene and pinene. This helps boost the uplifting effects of these strains. They generally have only small amounts of myrcene, which has a more sedating influence.
Digging into Indicas
Indicas are a bit shorter and bushier than Sativas. They have darker, broader leaves, and their buds are much chunkier. Indicas originated in India and parts of Asia. They crave light and certain amounts of heat, but they are acclimated to cooler temperatures, less direct sunlight, and constant breezes.
Many Indicas have a calming, relaxing effect. While they can contain moderate to high amounts of THC, their effects are completely different than those you would experience with Sativas. This is due in large part to the terpenes Mother Nature adds to the mix. Indicas typically have higher amounts of myrcene, which has a sedating impact of its own and enhances the relaxing effects of the other compounds in Indicas.
Ruderalis under the Microscope
Ruderalis is a small breed of cannabis that evolved in areas where other strains just could not thrive. These include parts of Asia and Europe as well as Russia. It grows short and sparse rather than tall or bushy because it arose in places where less heat and sunlight were available and growing seasons were decidedly brief.
Ruderalis is known for being much less potent than Indica and Sativa. It generally creates no THC during the growing process. Most growers do not seek out Ruderalis specifically unless they are looking for a hardy strain with a short growth cycle and few demands. This variety of marijuana is often used in the hybridization process to create autoflowering strains, though.
Terpenes vary in strains in the Ruderalis category though several of them are part of the overall picture. It is also safe to say that the terpenes in Ruderalis are not as strong as those in other strains since this variety is known for its lack of potency. Since Ruderalis naturally matures faster and has less sunlight to draw from, its terpenes and cannabinoids just do not develop as well as those of other strains.
Still, the ones that are there are bound to offer plenty of benefits in their own rights. They also aid in enhancing the terpene profiles of hybrids that contain Ruderalis DNA. They may be less powerful, but they should not be dismissed altogether.
Examining Hybrids
Hybrids are made by combining the DNA of various marijuana strains. This allows breeders to weed out some of the less desirable traits of those strains while bringing their more beneficial characteristics to the surface. For example, crossing a high-THC strain with one that has moderate levels of CBD can create a variety that still offers the high many users want without some of the unpleasant effects THC might bring about, such as paranoia.
In addition to providing adjusted amounts of THC and CBD and customized effects, hybridization affects the terpene profiles of the resulting plants. Since those ramped-up terpene profiles develop naturally, they are more effective and beneficial.
Those terpenes also work better together to give you a more enjoyable marijuana experience. If the terpenes were extracted from different strains and forced together in a lab, they certainly would not be as helpful because they were never meant to be combined. They would not have all the other compounds that naturally accompany them to foster the Entourage Effect, either.
These days, an endless list of hybrid cannabis strains has been developed, and it is only going to grow moving forward. Because of this, there is no clear-cut range of terpenes that are sure to be present in a specific variety. Still, Sativa- and Indica-dominant strains are bound to contain higher levels of pinene and myrcene respectively.
An In-Depth Terpene Analysis
At this point, we have explored some of the most common terpenes. We’ve also broken down weed into its primary strains and the basic terpenes found in each one. Now, let us take a closer look at some of the terpenes that might make their way into the profile of your favorite strains.
Primary Terpenes
Primary terpenes are those found in abundant amounts in various types of cannabis. They are also common in many different strains. Additionally, their effects tend to be a bit more noteworthy than secondary compounds.
Myrcene
Myrcene is one of the most common terpenes in the world of cannabis. It generates a pungent, skunky, earthy flavor and aroma. It also has a wide range of effects and benefits.
Just how much myrcene is present in a given strain and which additional compounds it is combined with determines its specific effects, but it generally induces relaxation. Strains with less than 0.5 percent myrcene are usually energizing and uplifting whereas those with higher amounts are sedating.
Myrcene is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory effects. This terpene is also an antibacterial agent and can provide relief from many types of pain. Strains with significant amounts of myrcene include Skunk XL, White Widow, and Special Kush. Myrcene is also found in mangoes, thyme, basil, and hops.
Limonene
Limonene has a citrusy taste and aroma. It is found in lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruits as well as many types of flowers. This terpene is famous for its sweet, refreshing, energizing effects. That is why it is often used in facial cleansers, soaps, and body washes. It also helps blast away sadness and foul moods because of its smell and physical influence, so it is great for treating anxiety and depression.
Sour Diesel, OG Kush, and Super Lemon Haze are a few of the most popular limonene-laden strains. Limonene is a powerful antibacterial agent, making it a perfect addition to household cleaners, dish detergents, and hand soaps. It also has antifungal properties and helps mitigate acid reflux and indigestion. Studies likewise show that limonene may aid in treating cancer and some of its symptoms.
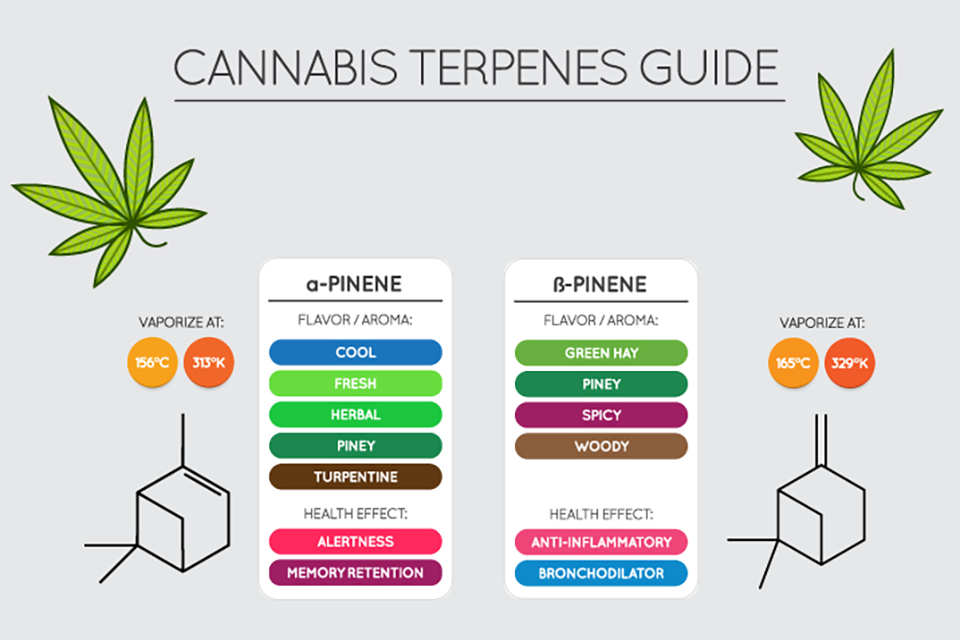
Pinene
Pinene has been deemed the world’s more prevalent terpene because it is found in so many places. These include pine trees, basil, rosemary, and citrus zest to name a few. It is also present in many strains of cannabis, and it makes itself known by emitting a robust earthy, pine-like scent with lovely spicy and herbal undertones.
Strawberry Cough and Blue Dream are a couple of strains with high concentrations of pinene. As far as benefits are concerned, pinene is an effective anti-inflammatory agent with antiseptic properties. It acts as a bronchodilator, making it helpful for those who suffer from asthma. It also helps create a sense of alertness.
Linalool
Many people consider linalool to be the standard weed terpene because its odor commonly brings to mind images of marijuana. It has a floral, spicy aroma and is found in many herbs and flowers. It also has a bit of a myrcene-like smell and works with this popular counterpart to create the basic familiar marijuana smell and taste.
Linalool fosters pain relief and relaxation. It is an antifungal and antibacterial component that helps reduce the frequency and severity of seizures. It may also be effective in the battle against cancer. On top of all that, linalool can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. Special Kush, Amnesia Haze, and OG Shark are a few of the strains that offer significant concentrations of this terpene.
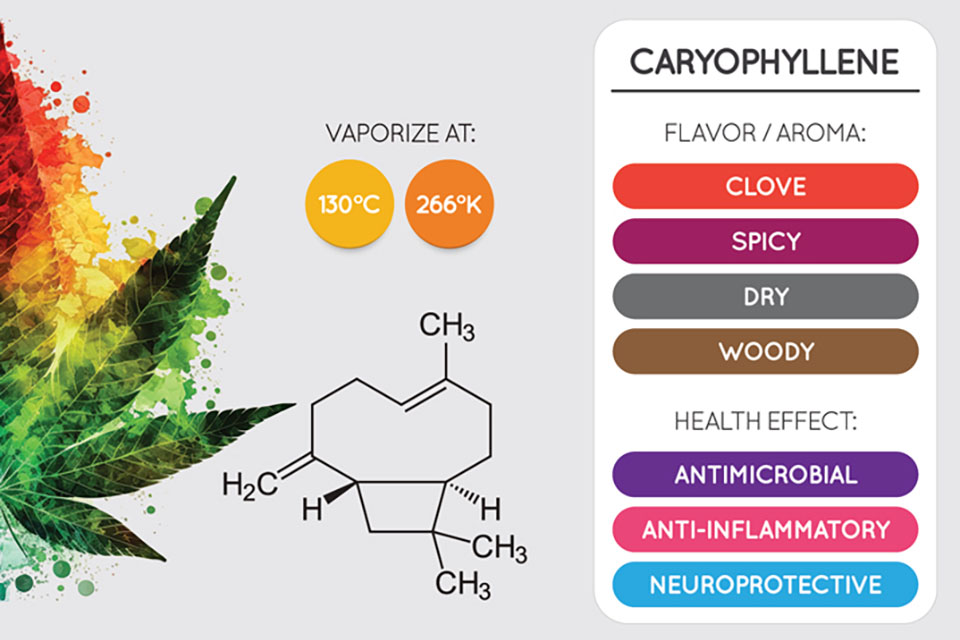
Caryophyllene
If you have ever caught a whiff of black pepper, cinnamon, or other sharply scented spices, you have experienced caryophyllene. It has a woody, peppery, spiced aroma that truly stands out. Strains like Super Silver Haze, Skywalker, and Rock Star are high in caryophyllene. Due to their ample amounts of this terpene, they can help with treating anxiety, depression, and inflammation.
Humulene
Humulene is often found in hops, one of the main components in beer. It also happens to smell a bit like beer with its earthy, woody notes. When combined with the other compounds in cannabis, it can produce many helpful effects. These include fighting bacteria and inflammation and serving as an appetite suppressant. You will find humulene in Liberty Haze, Girl Scout Cookies, and Sour Diesel among other strains.
Terpinolene
Terpinolene has a bit of a bite to it. It is found in tea tree oil and emits a floral, woody, herbal aroma with hints of lime. Super Lemon Haze, Jack Herer, and Pineapple Kush are a few of the strains that contain terpinolene. It acts as an antioxidant and an anti-cancer agent while offering sedative effects and relief from pain.
Nerolidol
Found in ginger, lavender, Mexican orchids, and jasmine, nerolidol is also common in marijuana strains like Jack Herer, Blue Dream, and Chemdawg. It has a floral, woody aroma many people associate with the heavy, pungent scent of the forest. It is an antifungal and antioxidant that provides a relaxing, sedating effect. It is often used to help induce sleep and fight anxiety.
Bisabolol
Also known as levomenol, bisabolol has a floral essence. It is found in chamomile and often used in perfumes. This terpene provides pain relief while helping to fight off bacterial and microbial infections. If you would like to experience bisabolol, you might want to try a strain like ACDC, Headband, or Pink Kush.
Guaiol
Guaiol, or champacol as it is sometimes called, has a fresh, stimulating fragrance that smells woody and a bit like roses. It is found in the guaiacum plant that is native to the Caribbean and South America as well as nutmeg and cumin. Royal Gorilla, Sour Berry, and Haze Berry are high in guaiol as well. It is known for its anti-cancer and antibacterial benefits.
Ocimene
Reports indicate that ocimene can offer a broad range of benefits. It provides antifungal and antiviral effects and helps reduce inflammation. This terpene has a sweet, herbal, woody aroma and is found in mint, parsley, and mangoes. It is also present in OG Kush, Sour Diesel, and Strawberry Cough.
Secondary Terpenes
Secondary terpenes are just as important as primary ones. They are not quite as common among different species, though. Various strains of cannabis generally contain smaller amounts of these terpenes.
Sabinene
Spices like black pepper and nutmeg are usually high in sabinene. It is also found in tea tree and some other evergreens. It is known for its woody, spicy scent and can calm digestive issues and certain types of skin inflammation.
Sabinene helps relieve inflammation and arthritis pain as well. It is not quite as prevalent in cannabis as other terpenes, but if your chosen strain has a slightly minty or peppery essence, it probably contains sabinene.
Phellandrene
Dill, wild parsnips, and eucalyptus are a few of the more common sources of phellandrene. It smells like peppermint with slight citrusy notes. While phellandrene may offer a number of beneficial effects, it is most often touted as an antidepressant.
Borneol
Borneol naturally occurs in artemisia, rosemary, valerian, and Scotch pine as well as some strains of cannabis that have earthy, minty, pine-like scents and flavors. It aids in pain relief and alleviating inflammation.
Isoborneol
Isoborneol serves as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory while offering antimicrobial properties. It may also help keep the herpes simplex type-1 virus at bay. This terpene has a musty, somewhat sweet smell. It is sometimes used as an insect repellent and can be found in a few cannabis strains, such as Golden Haze.
Phytol
Phytol is a terpene found in many types of green tea, so it is naturally a powerful antioxidant. It is also an effective sedative and can help fight stress and anxiety. Cheese and Sour Diesel are a couple of marijuana strains that are high in phytol. Though this terpene does not have the same strong, noticeable flavor and aroma as others, it is sometimes said to have a slightly grassy taste.
Keep in mind, these are only a few of the most common terpenes. At least 200 others have been unearthed in cannabis alone. As more research is conducted on these essential compounds, others are sure to come to light.
Which Strains Have the Highest Terpene Concentrations?
All cannabis strains have terpenes though not all of them contain the same types and amounts of these compounds. Considering the many hybrids on the market and all the factors that affect terpene content, it is difficult to say which ones have the highest concentrations and most well-rounded profiles. That said, we can give you a general idea.
Regular Cannabis Strains
Cannabis plants are dioecious, meaning they come in male and female forms. Studies show that unfertilized female plants have the highest concentrations of terpenes and cannabinoids, so regular female plants could be ideal for growers who are focusing on terpene profiles. Males tend to be a bit less potent.
Remember, though, if you are using regular strains, you have to keep an eye on them and separate the males from the females once they begin to mature. That means knowing how to differentiate between the two and being diligent in your plant care efforts. If a female plant is pollinated by a male, her potency drops significantly. Instead of using her stored compounds to create big, powerful buds, she uses them to develop seeds.
Feminized Marijuana
Since unfertilized female marijuana plants have the highest levels of potency, feminized cannabis is a great choice for over-the-top terpene concentrations. Feminized plants are created without the use of male DNA, so they are virtually guaranteed to be female. With a batch of feminized seeds, you do not have to worry about male plants sprouting up, pollinating the females, and ruining the potency of your crop.
Autoflowering Strains
When it comes to terpene and cannabinoid concentrations, autoflowering strains are the weakest. They have certain amounts of these compounds, but not as much as other types of cannabis. This reduced potency occurs because autoflowering strains have Ruderalis DNA added to their genetic profiles.
They will stand up to less favorable growing conditions and be ready for harvest much earlier, but they just will not give you ample amounts of terpenes or other components. If you are concerned with potent terpenes but have your heart set on growing autoflowering marijuana, choose your seeds carefully.
Best Terpenes for Medicinal and Recreational Uses
Terpenes have different effects, and their concentrations and accompanying components can alter their impacts significantly. If you are seeking cannabis for medicinal purposes, the ones with terpenes that provide anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties would be your best bet. These include pinene, linalool, ocimene, and terpinolene among many others.
For those who use marijuana recreationally, an entirely different set of terpenes is important. You should be aware that myrcene can make or break a high depending on how much of it is present in a specific strain. Low concentrations can provide beneficial impacts and enhance a cerebral high while high concentrations can completely negate the entire experience and put you right to sleep.
How Are Terpenes Extracted?
Terpenes develop within the cannabis plant. When you smoke your favorite strain, you are naturally drawing all the terpenes, cannabinoids, flavonoids, and other compounds into your body. From there, it processes all those components and uses them as needed.
If you are looking to take the terpenes out of cannabis plants for use in edibles, tinctures, topicals, and other products, the matter becomes a bit more complicated. Several processes can be used for terpene extraction. They are the same processes used to draw essential oils out of other botanical materials from Douglas fir to frankincense.
Butane Hash Oil
One of the most commonly used extraction methods involves using butane, heat, and pressure to draw out the terpenes from the cannabis plant. Raw botanical materials are placed in glass containers. From there, they are exposed to a butane solvent, and heat and pressure are applied to pull the terpenes and other components out of the plant material.
Once the compounds are extracted, they are exposed to cold temperatures to separate any remaining solvent and impurities from the desired components. The butane that evaporates during extraction collects in a vacuum unit while butane hash oil is left behind. BHO is a hard, yellowish substance that contains all the good compounds extracted from the cannabis plant material.
Butane-based extraction is a cost-effective option that quickly produces high yields. Unfortunately, it can also be dangerous without the right equipment and training. Product contamination is also a concern with this method because of the butane used for extraction. After all, you want to use butane to light the weed, not to ingest it along with all the good stuff. As long as you know what you are doing and exercise caution with butane extraction, though, there should not be any problems.
Ethanol Extraction
In ethanol extraction, alcohol is used to draw out the desired components in cannabis. This is one of the earliest extraction processes known to mankind. It uses the same type of alcohol we drink but without any fancy flavors or colors added to it. Ethanol can potentially affect the flavor and smell of the resulting extracts, but it is not as likely to as butane. There is less concern over contamination with ethanol as well.
On the other hand, certain disadvantages arise with traditional ethanol extraction. Though the alcohol itself is not as likely to affect the essence of the cannabis, its chemical composition can work against you. Since ethanol binds to the cannabinoids and terpenes in marijuana as well as the chlorophyll and impurities, those undesirable elements may end up lingering in the finished product. This could make it look, taste, and smell considerably less appealing.
New methods have been developed in recent years to help mitigate the downsides of ethanol extraction. Microfiltration aids in getting rid of the impurities and other unwanted components while keeping the compounds you want. Ethanol extraction is considered a more time-consuming and less efficient process than BHO and other alternatives, but cryotemperatures are now being used to improve those aspects.
C02 Extraction
Many cannabis product producers are turning to the CO2 extraction method. You could say this process combines the benefits of butane and ethanol extraction without bringing some of the disadvantages into the mix. With this type of extraction, gaseous CO2 is transformed into a liquid via heat and pressure. Then, it is mixed with botanical materials to draw out the inner compounds.
As is the case with butane extraction, the resulting extracts need to be exposed to low temperatures, or winterized, afterward. In line with ethanol extraction, the solvent can bind with impurities as well as desired compounds, so additional purification is required to create a higher-quality product. All that means you could lose more of the terpenes, so your end product may not be quite as potent.
CO2 extraction is not as fast and efficient as the butane-based method, but it is not as potentially dangerous, either. You will not run into the same possible hurdles as you might with ethanol extraction. This process is often more expensive than others, though, so cost could be an issue.
Live Resin
Live resin entails using either butane or CO2 extraction though the process is a bit different than the norm. With standard butane and CO2 extraction, the plant materials and solvents are exposed to high temperatures. When using the live resin method, the buds are kept frozen throughout the process. Then, impurities are removed from the extracts using a low-temperature vacuum system.
Since high temperatures are not used with live resin extraction, you do not run the risk of losing as much of the valuable cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, and other components as you would using other techniques. At the same time, the refining process does not further destroy the desirable compounds. Live resin production creates a potent, high-quality product, but it is not as fast or affordable as standard butane extraction.
Solventless Extraction
Not all extraction processes require chemical solvents. Solventless techniques work using steam or water. Steam distillation works by placing a container of raw botanical material over a container of boiling water. This causes steam to gather in the plant material. In turn, the plant material releases its essential oils.
Those oils and steam funnel into a condenser where they cool. There, the steam returns to its liquid form, which is water, and the oils float to the surface of the water where they can be skimmed off and used for various purposes. Hydro-distillation works in much the same way, but the plant material is placed directly in water, and the terpenes and other components are essentially boiled out of it.
This method may seem crude and simplistic when compared to more modern and advanced extraction techniques, but it offers a few advantages. For one, since it does not require chemical solvents, there is no chance of contaminating the finished product.
Secondly, it is safe as long as you take care not to burn yourself while using heat to steam or boil the plant material. With steam extraction, you do not have to worry about diluting the essential oils, either.
Solventless extraction methods come with a major downside, though. Because they involve heating the plant material, they often destroy many of the sought-after cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes in the process. They may not dilute the final product, but they could render it less potent than it should be and lead to a less hearty flavor and aroma profile.
Which One Is Best?
All of these terpene extraction methods are effective. Each one also has its share of downfalls. Butane extraction is generally less expensive and more productive, but it could leave contaminants in your product. It can also be hazardous under the right circumstances, such as using open-tube systems instead of closed.
CO2 extraction is safer than methods that use butane as a solvent, but this process is more expensive and generally yields less product. You could end up with unwanted impurities as well. This is also true of ethanol extraction although this alternative has seen quite a few improvements lately.
Live resin preserves more of cannabis’ natural terpenes and cannabinoids, but it is one of the most expensive solutions. Solventless extraction does not leave behind contaminants, yet it requires high temperatures. That means it could destroy many of the compounds you want to keep intact.
Overall, the best extraction method for you depends on a range of considerations. Your budget for extraction equipment is one of the most important. What you will be using the extracts for is another. How much product you are expecting to get from the raw material matters as well.
Interesting Facts About Terpenes
- Terpenes are complex and intriguing compounds. They can provide any number of benefits especially when combined with other components. Their benefits are magnified if they are natural as opposed to synthetic.
- In general, plants with more than 0.5 percent myrcene are said to be indica, while those with less than 0.5 percent myrcene have more uplifting, sativa-type influences. Of all the terpenes, ccaryophyllene is the only one known to act directly on the endocannabinoid system. This is the one found prominently in black pepper and has yields anti-inflammatory properties when bound to CB2 receptors in the body.
- People have been using terpenes to ease certain ailments and improve their states of mind for centuries. It is called aromatherapy. This was a popular form of treatment long before terpenes began making headlines. Anytime you use perfume, cologne, scented bath products, or lotions, you are employing terpenes.
- You may remember the infamous color wheel from elementary school art class. There is actually a terpene wheel as well. It lists numerous terpenes as well as their scents, flavors, and benefits.
- We have mentioned that more than 200 terpenes have been found in cannabis so far. You might be surprised to learn that there are tens of thousands of terpenes in other plants. With that in mind, there is no end to the possible combinations and interesting facts surrounding these amazing compounds.
How to Maximize Terpene Production in Your Plants
As we alluded to previously, several factors can contribute to or detract from the terpenes in your cannabis crop. One of the most effective steps you can take to maximize the terpene concentration and profile is to start with premium seeds like those we have to offer here at Kind Seed Co.
Indoor Growing Versus Outdoor Growing
Whether you grow your weed crop indoors or outdoors can make a significant difference in its terpene profile and overall potency. Many people swear outdoor cannabis is better all-around than plants that are grown indoors. This mainly comes from the growing conditions. Mother Nature provides everything the plants need to develop well-rounded profiles outdoors, but the responsibility is on the shoulders of the grower for indoor crops.
With an indoor marijuana garden, regulating the amounts of heat, humidity, water, and nutrients the plants receive becomes extremely important. Without those factors, they will not thrive and give you a bountiful bud harvest. In terms of terpene development, light is the most important element. Being sure the plants get just the right types and amounts of light at the perfect times will determine how robust their terpenes are.
Other Considerations
It is also crucial to plant your marijuana seeds in nutrient-rich soil or growing media. During the early stages of cannabis’ life cycle, use a fertilizer with plenty of nitrogen. When they enter the flowering phase, they need more phosphorus to develop potent buds with enhanced terpene concentrations.
Though the plants often need fertilizers for optimal nutrient availability, it is important to give them brief periods without added ingredients in the soil as well. This helps avoid overfertilization, which could be just as detrimental as not giving them any nutrients at all.
Be sure to give the plants a little extra water or flush out your hydroponic system during those times when you do not add fertilizer. Do not get overzealous when harvest time approaches, either. Be sure to let the buds reach full maturity before plucking them. From there, be careful with your drying or curing processes to avoid destroying vital terpenes and cannabinoids.
Bottom Line
Terpenes give marijuana its flavors and aromas while also providing a wide range of potential benefits. Not all marijuana plants have the same potency or terpene profiles. How they are grown can have a significant impact on their terpene concentrations as well.
Now that you know everything you need to know about terpenes, it is time to start growing. Browse through our extensive inventory of high-quality wholesale cannabis seeds to see which ones might suit your needs and preferences.
At Kind Seed Co, we offer a variety of strains that are sure to meet your expectations whether you are looking for medicinal terpene profiles or purely recreational alternatives. Call US or email us with any questions you may have. Be sure to check out all the helpful resources we have made available for cannabis growers as well.